T1/E1/PRI ISDN Gateway
Transport your enterprise phone system to the world of IP Telephony with the SN4170 T1/E1/PRI Gateway. Supports up to 30 concurrent G.711/ G.722 voice/fax calls with secure HTTPS, stateful firewall, and TLS/SRTP. |
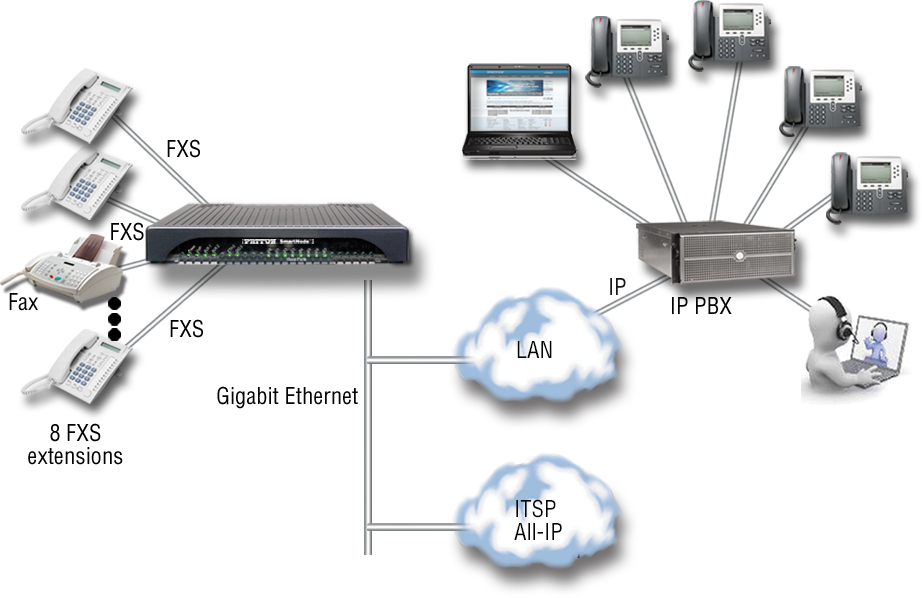
Analog Gateway with 2, 4 or 8 FXS/FXO ports
The SmartNode 4140 Series of VoIP Analog Gateway products support up to eight telephone connections integrating legacy equipment into a UCC environment. High-quality voice and reliable fax over any IP network. All-IP does not end when analog terminals have to be integrated. Security and quality guaranteed. |
SS7 TDM-to-IP Media Gateway with T1/E1/J1
The carrier-grade SmartNode 10100 SS7 gateway supports 128 to 256 calls. Smaller service providers can use this SS7 gateway to drive convergence between TDM and IP networks. The SN10100 carrier gateway replaces multiple devices for signaling, connectivity, and media transcoding. |
ISDN-to-IP Gateway with 2, 4 or 8 BRI S0 ports
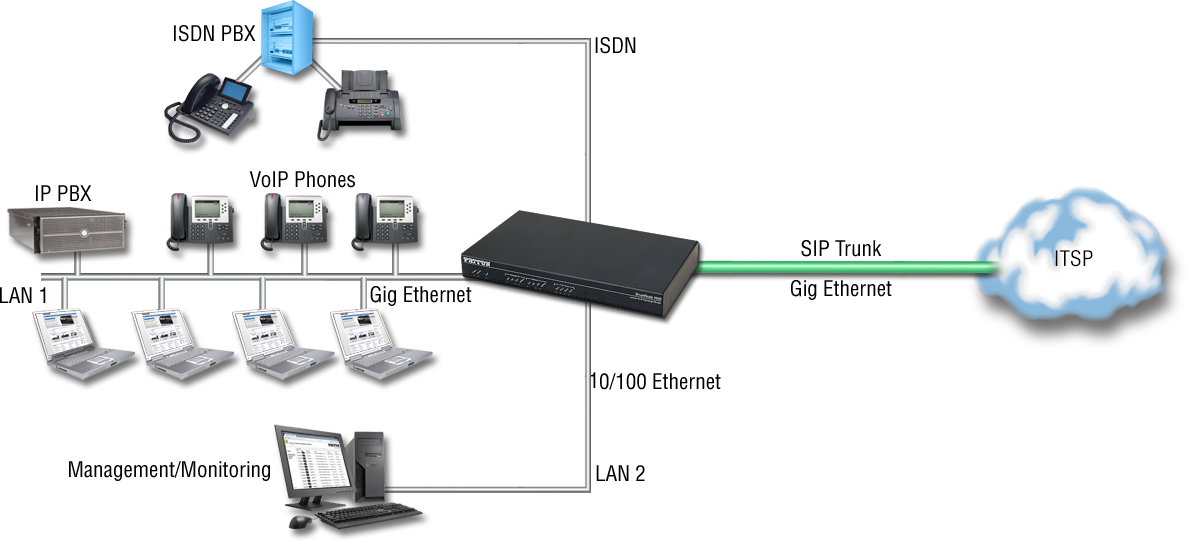
With up to 4 BRI ports and 8 simultaneous G.711 voice channels, the SN4130 is the best way to connect ISDN networks or ISDN terminal equipment to the world of voice over IP. It supports up to 5 G.711 or up to 8 G.722 voice/fax calls concurrently with secure HTTPS, stateful firewall, and TLS/SRTP. |


|
Company > Contact Us > About Patton > Jobs > Capabilities > Quality & Responsibility > Legal News & Events > Press Room/Releases > Training & Events > Library/Downloads |
| Sitemap |
Legal |
Privacy Policy |
Disclaimer |
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()