Go Directly to the Products >>>
What is a Media Gateway? How does a Digital Media Gateway or SIP Media Gateway work?
A Media Gateway is a networking device that provides valuable and essential functions for organizations, service providers, and network operators. When interconnecting traditional time-division-multiplexed (TDM) telephony systems with modern voice-over-internet protocol (VoIP) systems, a VoIP media gateway works by providing protocol conversion (translation) and interoperability between the two network technologies. Also known as an IP media gateway or SIP media gateway, the device converts a traditional analog plain-old-telephone-system (POTS) voice signal or related digital telephony signals such as T1, DS3, STM1 or OC3 into packets for transmission over a data network such as the Internet, private IP Network or a corporate LAN. When the legacy system is based on digital integrated services digital network (ISDN) technology, the device may be called a digital VoIP gateway or ISDN media gateway. Some manufacturers combine gateway functionality with WAN-access (internet-access) capability into a single device or network appliance. Such a dual-purpose device may be known as an access media gateway.
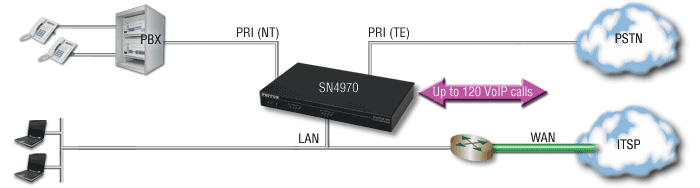
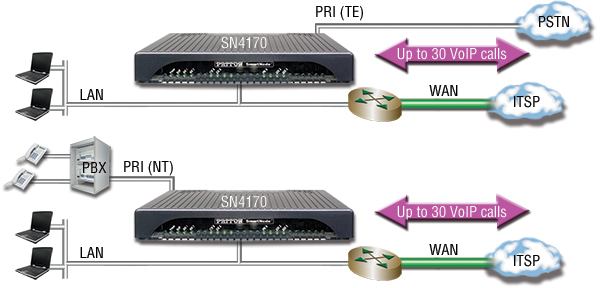
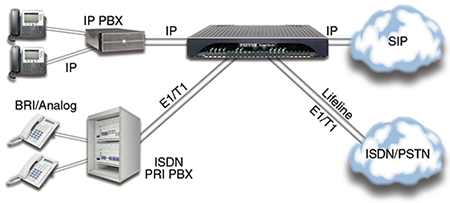
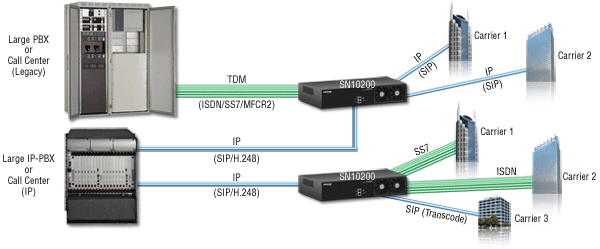
Many organizations are replacing their traditional public-switched-telephone-network (PSTN) trunk lines (T1/E1/PRI) with voice-over-IP (VoIP) trunks. Since the most popular modern VoIP protocol today is the session initiation protocol or SIP, the VoIP trunk is usually called a SIP trunk and the gateway may be called a trunk media gateway. The diagram below shows a SIP trunk gateway within a VoIP network application.
 Media Gateway in a SIP trunk Application
Enterprise Applications
Media Gateway in a SIP trunk Application
Enterprise Applications
Any size enterprise can use a media gateway to transition gradually from legacy circuit-switched, time-division-multiplexed (TDM) infrastructure to packet-switched internet-protocol (IP) network architecture. When embarking on ALL-IP network transformation, a SIP gateway is an essential element.
Businesses normally use VoIP gateways to extend the life of traditional TDM gear--including legacy PBXs, analog phones, and analog lines for elevator phones, alarm systems and fax machines--while gradually implementing IP-based technologies. Corporate IT organizations can use media gateways to:
- Augment or replace a traditional analog or digital PBX system with SIP trunk service
- Connect legacy equipment to new IP networks
- Protect and extend investments in TDM and analog devices
- Preserve the useful life of existing telco-line equipment
- Avoid costly rip-and-replace upgrades
Telecom Applications
Many network operators today maintain legacy TDM and modern IP networks concurrently, with interconnections between them. A telecom media gateway provides protocol conversion and interoperability between the two disparate networks. Often another device, known as a media-gateway controller, is employed to provide signaling and call control for the telecom gateway using the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) standard Media Gateway Control Protocol (MGCP). Such a hybrid service provider network architecture is depicted in the drawing below.
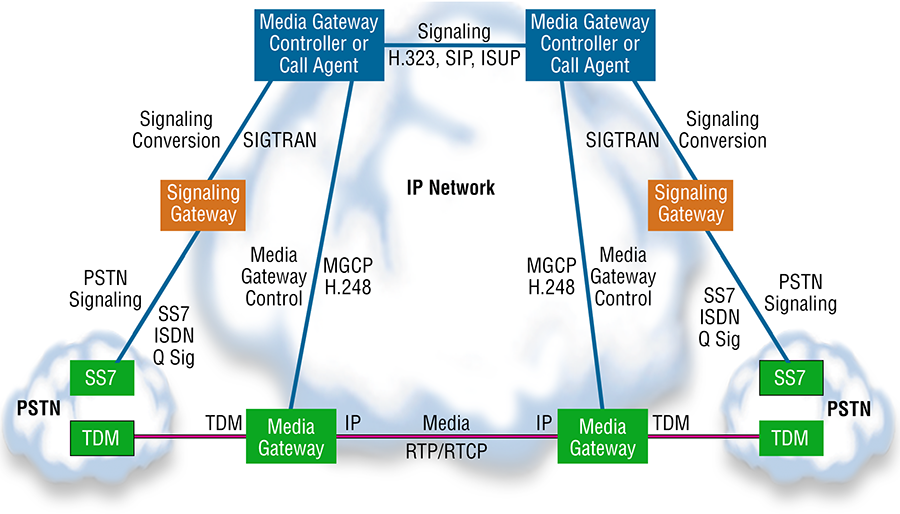 Hybrid Media Gateways in a Service Provider network
Hybrid Media Gateways in a Service Provider network
Network operators, mobile, and fixed-line service providers often use media gateways to:
- Perform IP-to-IP media conversion for converged networks
- Deliver SIP-based services to legacy TDM-based customers
- Replace legacy TDM central office switches


 Hybrid Media Gateways in a Service Provider network
Hybrid Media Gateways in a Service Provider network
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()